

If the test is positive, an ultrasound is scheduled two to three weeks later. The remaining embryos may be cryopreserved (frozen) for possible future embryo transfer.įor more information on The Fertility Clinic protocols, please take a look at our “ Protocols and Procedures” in the “Patient Information” section.Īfter the eggs retrieval, daily progesterone supplementation is administered to increase the chances of pregnancy.Ī pregnancy test is performed two weeks after egg retrieval. Three to five days after the retrieval, the fertilized eggs (now embryos) are placed into the uterus with a small catheter. Fertilization can also be accomplished by ICSI if there is an expected low rate of fertilization with conventional IVF or a known male factor. The eggs are examined under the microscope and a few hours later, they are combined with the sperm in a culture dish to allow natural fertilization to occur.

The eggs are examined under the microscopy and, a few hours later, they are combined with the sperm in a culture dish to allow natural fertilization to occur.can also be accomplished by if there is an expected low rate of fertilization with conventional IVF. The procedure is about thirty minutes long and is generally well tolerated.
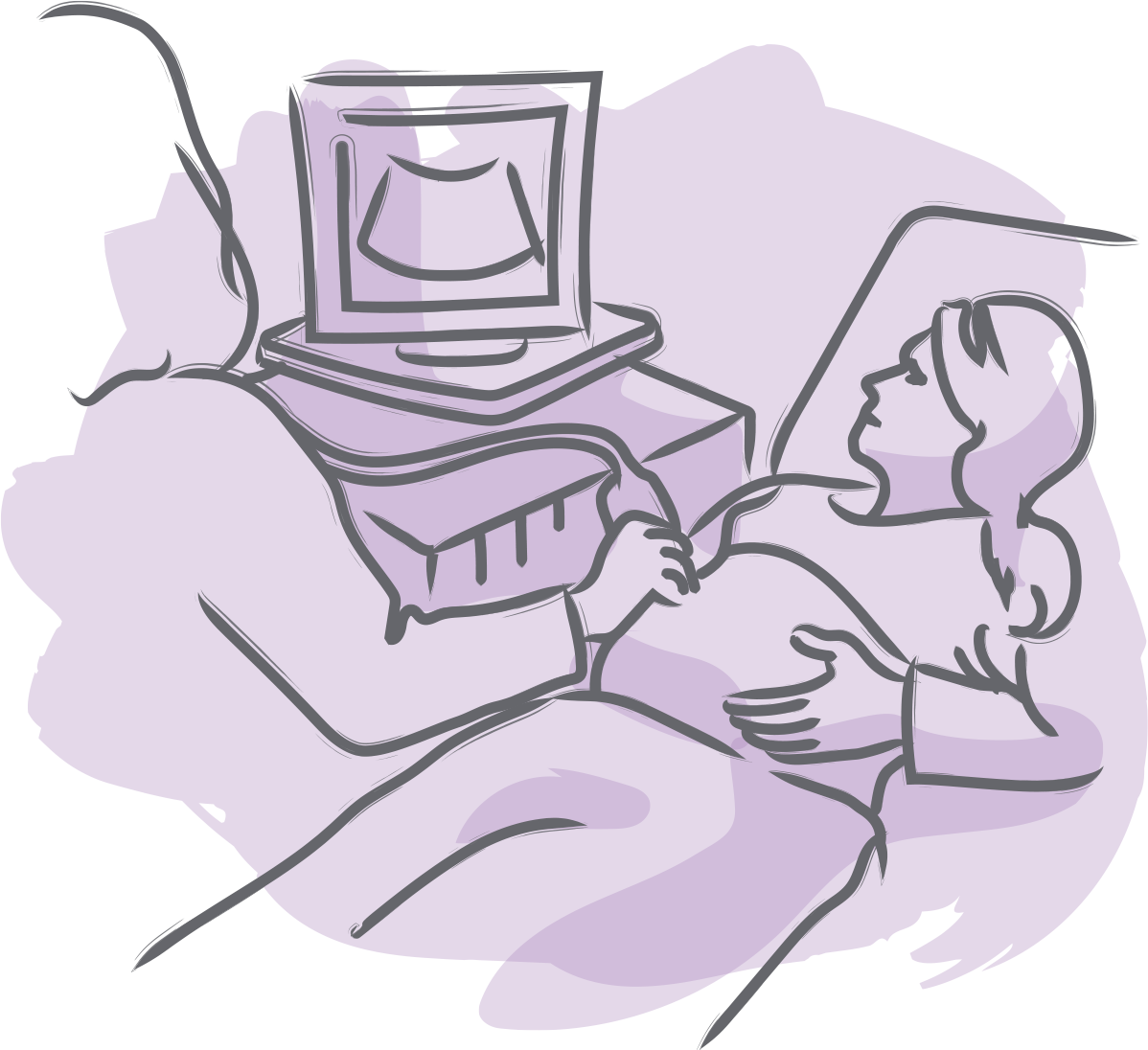
With the use of transvaginal pelvic ultrasound guidance, a needle is inserted through the vagina into the ovaries to collect the follicular fluid containing the eggs. When the ultrasound reveals that the eggs are mature, a single injection of human Chorionic Gonadotropin ( hCG) is required to induce the final maturation of eggs.Īpproximately 36 hours after hCG injection, the egg retrieval is performed under conscious sedation. However, several recent studies have been overall reassuring. In addition, fertility drugs have been associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer. Gonadotropins ( FSH, LH) therapy is associated with a risk of multiple pregnancies as well as with a risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). Most patients also continue with GnRH agonist or antagonists to prevent premature ovulation prior to egg retrieval.ĭuring the stimulation phase, frequent monitoring by transvaginal ultrasound and blood tests are necessary to examine the ovaries and to measure hormone (E2 and LH) levels. In this phase, which lasts approximately 10-14 days, the ovaries are stimulated with daily injections of Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and, in selected cases, with Luteinizing Hormone (LH) to produce multiple follicles, each containing one egg. Transvaginal pelvic ultrasound is commonly used during this time to assess the presence of cysts Possible oral contraceptive pill (OCP) for a few weeks to allow more flexibility in the timing of the cycle (the number of days on OCP can be varied) and to reduce the chance of ovarian cyst development, which can interfere with treatment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
